 Many people around the world suffer from insomnia. In the United States alone, it is estimated that 60 million Americans experience some kind of sleep disorder. There are many debates about how to best treat those who experience chronic insomnia.
Many people around the world suffer from insomnia. In the United States alone, it is estimated that 60 million Americans experience some kind of sleep disorder. There are many debates about how to best treat those who experience chronic insomnia.  A variety of medications have been introduced, among other kinds of treatments. Drugs that are meant as sleeping pills or aids are known as hypnotic drugs. This terminology comes from the Greek word “hypnos”, meaning sleep. Ambien® is one of these hypnotic drugs that is used to help individuals with insomnia or other conditions that inhibit sleep. Ambien is used as a prescription drug only for short periods of time. The drug rose out of a desire for a wider variety of hypnotic drug options that had less severe side effects in comparison to narcotic counterparts. However, further widespread public use of Ambien has proven that this drug still retains some serious side effects. Additionally, long-term use of this drug, or recreational use, can lead to dependency and addiction for a user. Understanding the challenges posed by the serious side effects of Ambien can help you or a loved one know what to expect from prolonged or recreational drug use. If you find yourself addicted to Ambien or any other kind of sleep aid, Northpoint Washington is here to help with our personalized and integrated treatment care program. Treatment for Ambien addiction is available here.
A variety of medications have been introduced, among other kinds of treatments. Drugs that are meant as sleeping pills or aids are known as hypnotic drugs. This terminology comes from the Greek word “hypnos”, meaning sleep. Ambien® is one of these hypnotic drugs that is used to help individuals with insomnia or other conditions that inhibit sleep. Ambien is used as a prescription drug only for short periods of time. The drug rose out of a desire for a wider variety of hypnotic drug options that had less severe side effects in comparison to narcotic counterparts. However, further widespread public use of Ambien has proven that this drug still retains some serious side effects. Additionally, long-term use of this drug, or recreational use, can lead to dependency and addiction for a user. Understanding the challenges posed by the serious side effects of Ambien can help you or a loved one know what to expect from prolonged or recreational drug use. If you find yourself addicted to Ambien or any other kind of sleep aid, Northpoint Washington is here to help with our personalized and integrated treatment care program. Treatment for Ambien addiction is available here.
Commonly Used Hypnotic Drugs: Past and Present
There were a variety of commonly used hypnotic drugs in the 90s and preceding decades. Benzodiazepines, for example, were just one way that people treated insomnia. You might recognize the name Valium® as being a very commonly used drug, even becoming something of a household name and referenced commonly in movies and TV shows. Benzodiazepines, also simply referred to as benzos, are a particular type of substance that unfortunately is also highly associated with substance overdose. Not all benzos are illicit drugs. Some in fact, such as Valium, can be prescribed by a doctor and used effectively in treating various conditions when use is properly supervised.  Also common were various barbiturates, including Nembutal®. Barbiturates are a class of drugs that act as central nervous system depressants. That means that it reduces or calms nervous system activity. Barbiturates promote muscle relaxation and can also help lower heart rates and breathing, making them quite common in treatment for insomnia. While these drugs were effective for many, there were some serious consequences of relying on these substances to help treat insomnia. For example, these medications can often be a cause for concern when it comes to addiction and dependency. Other common concerns include the overbearing qualities of these substances, which can cause daytime drowsiness and over-sedation in some users. Both various benzos and barbiturates used to treat insomnia were quite potent, thus making them effective. Unfortunately, the potency of these drugs is also a downside, especially considering the fact that while individuals could counteract insomnia with these medications, daytime drowsiness somewhat undermined the goal of a good night’s sleep. Instead of just being tired when it was time for bed, people were tired throughout the day.
Also common were various barbiturates, including Nembutal®. Barbiturates are a class of drugs that act as central nervous system depressants. That means that it reduces or calms nervous system activity. Barbiturates promote muscle relaxation and can also help lower heart rates and breathing, making them quite common in treatment for insomnia. While these drugs were effective for many, there were some serious consequences of relying on these substances to help treat insomnia. For example, these medications can often be a cause for concern when it comes to addiction and dependency. Other common concerns include the overbearing qualities of these substances, which can cause daytime drowsiness and over-sedation in some users. Both various benzos and barbiturates used to treat insomnia were quite potent, thus making them effective. Unfortunately, the potency of these drugs is also a downside, especially considering the fact that while individuals could counteract insomnia with these medications, daytime drowsiness somewhat undermined the goal of a good night’s sleep. Instead of just being tired when it was time for bed, people were tired throughout the day.
Ambien Enters the Picture
As the serious consequences of using potent medications such as Valium and Nembutal began to become more noticeable, there was an increase in the desire for a drug that could be used in treating insomnia without as many severe side effects.  Ambien, also known sometimes as zolpidem tartrate, is a drug that was introduced in the 90s as an alternative to heavier narcotic solutions for insomnia. Ambien was quick to join the ranks of other hypnotic drugs that seemed to have less severe side effects for the user, yet remained effective at treating and managing insomnia. The drug became very popular and remains quite popular and commonly prescribed to this day. It was marketed as an effective drug for short-term use that a person could use without fear of serious consequences. However, the longer the drug was used by the general public, the more information came out about the serious side effects that Ambien could cause in some users. Since this drug has been out on the market for several decades now, health professionals have a better understanding of how Ambien can affect users. One should note that Ambien is generally prescribed for short-term use as a sleep aid for individuals who experience insomnia. The risk of experiencing more severe side effects is increased when Ambien is used for a prolonged period of time or used recreationally, meaning when a user does not intend to use the drug as a sleep aid.
Ambien, also known sometimes as zolpidem tartrate, is a drug that was introduced in the 90s as an alternative to heavier narcotic solutions for insomnia. Ambien was quick to join the ranks of other hypnotic drugs that seemed to have less severe side effects for the user, yet remained effective at treating and managing insomnia. The drug became very popular and remains quite popular and commonly prescribed to this day. It was marketed as an effective drug for short-term use that a person could use without fear of serious consequences. However, the longer the drug was used by the general public, the more information came out about the serious side effects that Ambien could cause in some users. Since this drug has been out on the market for several decades now, health professionals have a better understanding of how Ambien can affect users. One should note that Ambien is generally prescribed for short-term use as a sleep aid for individuals who experience insomnia. The risk of experiencing more severe side effects is increased when Ambien is used for a prolonged period of time or used recreationally, meaning when a user does not intend to use the drug as a sleep aid.
Physical Side Effects of Ambien Use
While Ambien serves many as a sleep aid to combat insomnia and provide relief without the serious side effects of barbiturates, like any other drug, there are a variety of side effects that a user can experience. 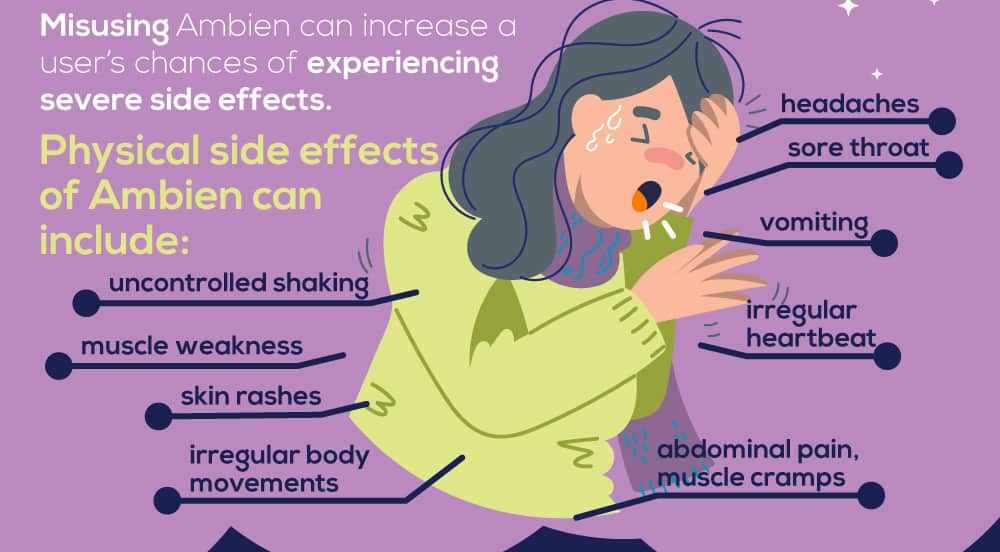 Usually, people who take the medication according to the prescription instructions can experience the positive effects of the medication. However, turning to Ambien as a means of relaxation or escape from the anxieties of life can constitute Ambien misuse. Misusing a substance by taking it when it’s unneeded, or taking larger and more frequent doses of the medication can increase a user’s chances of experiencing more severe side effects. Physical side effects of Ambien can include
Usually, people who take the medication according to the prescription instructions can experience the positive effects of the medication. However, turning to Ambien as a means of relaxation or escape from the anxieties of life can constitute Ambien misuse. Misusing a substance by taking it when it’s unneeded, or taking larger and more frequent doses of the medication can increase a user’s chances of experiencing more severe side effects. Physical side effects of Ambien can include
- Very fast or irregular heartbeat
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Lightheadedness
- Headaches
- Sore throat
- Abdominal pain
- Seeing double
- Muscle cramps
- Muscle weakness
- Skin rashes
- Irregular body movements
- Uncontrolled shaking
- Drowsiness
- Pinpoint pupils (pupils that have constricted to a small size)
- Slow and ineffective breathing (respiratory depression)
Some individuals can also experience an allergic reaction to this drug. An allergic reaction is characterized by symptoms that include swelling of the face, tongue, or mouth, shortness of breath, and breaking out in hives. Individuals who believe they may be experiencing an allergic reaction to the medication should seek immediate medical treatment.
Cognitive Side Effects of Ambien Use
Ambien is a drug that was specifically designed to replace commonly used benzodiazepines in insomnia treatment. The goal of Ambien was to try and steer users away from the potential of falling into the cases of addiction and substance misuse that sometimes occurred with benzos. Therefore, Ambien had to be a drug that could replicate the positive effects that benzos created without being as likely a drug for addiction and misuse. Ambien works by acting on receptor cells in the brain. Those receptor cells bind with a brain chemical called gamma-aminobutyric acid, or GAMA. This chemical helps influence and manage sleep and various neurological processes. Because of the drug’s interactions with this chemical in the brain, upon taking Ambien, it is possible that some users may experience various cognitive side effects. 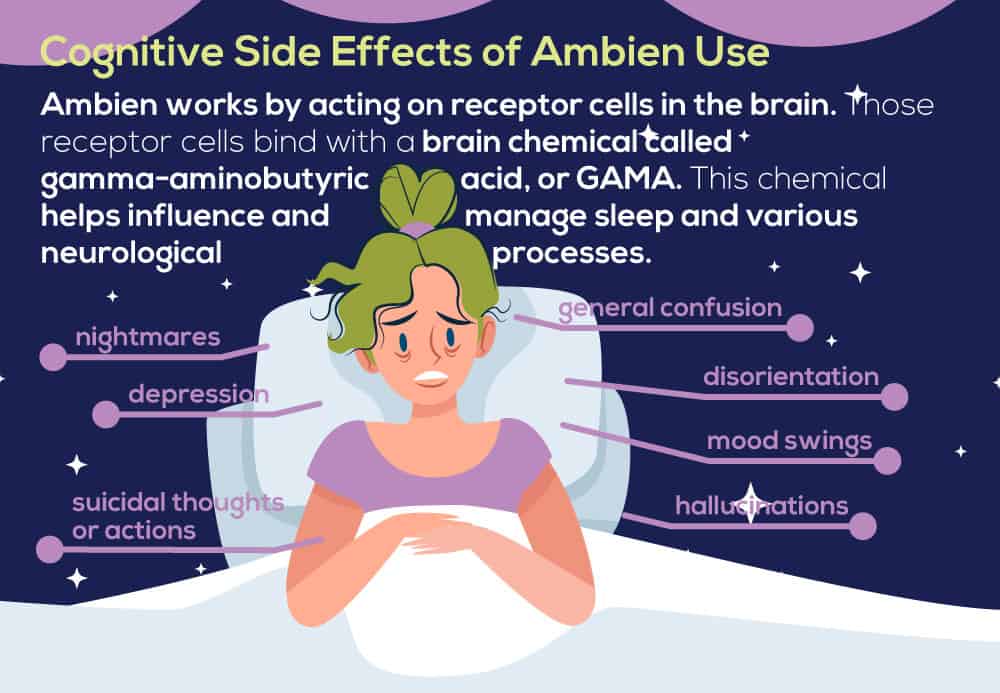 These cognitive side effects of Ambien can include
These cognitive side effects of Ambien can include
- Trouble concentrating
- Memory loss (amnesia)
- Disorientation, especially about place or time
- General confusion
- Loss of appreciation or pleasure about life
- Depression
- Suicidal thoughts or actions
- Anxiety
- Mood swings
- Nightmares
- Hallucinations
- Disturbances in sleep
- Inability to get a restful night’s sleep
Intensified Adverse Effects
As we’ve discussed, Ambien was created out of a demand for a sleep aid that could have less severe effects than other popular treatments, including the use of benzos. One of the primary arguments against treatments such as benzos was the occurrence of daytime sleepiness in users. Although Ambien was intended to offset such experiences, it appears that when taken in high doses, Ambien can remain in a user’s system the morning after a dose is taken. If a dose of the prescription is high enough, the influences of the drug can still affect someone waking up after taking the medication the night before. If the effects of the medication are strong enough, this can pose a great danger to some individuals who may still be experiencing drowsiness, lightheadedness, or dizziness, but need to drive to work in the morning. The possibility of severely adverse side effects is part of the reason why the FDA recommends that Ambien doses be limited.  The FDA also warns that, “Patients who take insomnia drugs can experience impairment of mental alertness the morning after use, even if they feel fully awake.” According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, individuals who take Ambien could experience the effects of sedation for up to 16 hours after the initial dose. Other adverse side effects of Ambien can include
The FDA also warns that, “Patients who take insomnia drugs can experience impairment of mental alertness the morning after use, even if they feel fully awake.” According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, individuals who take Ambien could experience the effects of sedation for up to 16 hours after the initial dose. Other adverse side effects of Ambien can include
- Excessive sedation
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Hallucinations
- Lack of proper motor control and coordination
- Slow response times
- Delayed reflexes
- Impaired judgment
- Increased aggression
- Clumsiness
When Ambien is initially taken, some users can also experience an initial boost of energy and feelings of euphoria. For some users, this feeling is what makes Ambien a drug of choice to be misused and taken in unnecessary frequent, high doses. After the initial rush of euphoric feelings, a user will experience the typical effects of drowsiness and can experience dizziness or poor coordination. When misused at a high dose, a user is at a higher risk of being involved in a bad fall, breaking or fracturing a bone, or being involved in some other kind of accident. 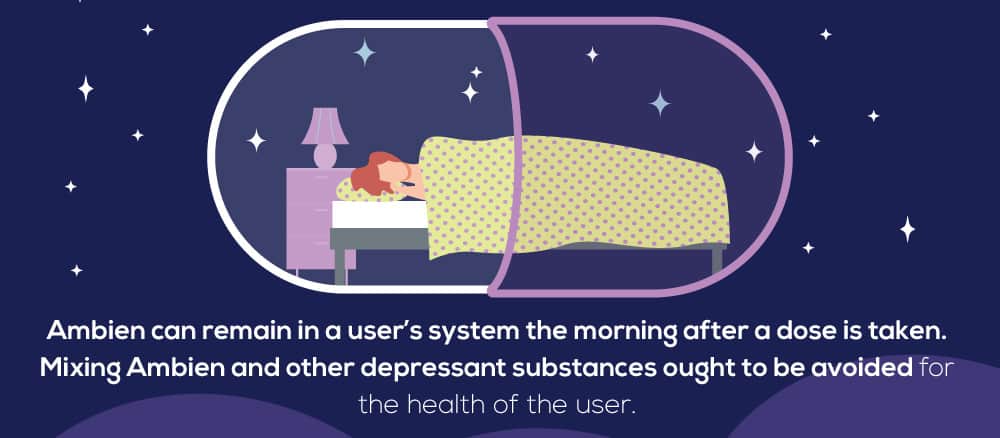 Mixing Ambien and other depressant substances ought to be avoided for the health of the user. Substances that depress the central nervous system include drugs such as alcohol, opioids, and tranquilizers. In combination with Ambien, the sedative effects Ambien will be amplified. This can increase the risk of fatal overdose and injury from accidents.
Mixing Ambien and other depressant substances ought to be avoided for the health of the user. Substances that depress the central nervous system include drugs such as alcohol, opioids, and tranquilizers. In combination with Ambien, the sedative effects Ambien will be amplified. This can increase the risk of fatal overdose and injury from accidents.
Unconscious Behaviors During Ambien Use
A variety of unconscious behaviors have been observed in some Ambien users. The following experiences and behaviors may not occur to all individuals. However, it can happen to some people and is more likely to occur when Ambien is misused or taken at a high dose. 
Sleepwalking
In the case of sleepwalking and other complex activities undertaken while on Ambien, the user is usually not aware that such activities are occurring. While sleepwalking, individuals will walk around and may even complete tasks while remaining in a state of sleep. Sleepwalking is a condition that is most commonly seen in children, but some other conditions, in this case substance-related, can cause sleepwalking in teens and adults. Clinically, activities undertaken in this state are referred to on a whole as parasomnia. Parasomnia is a condition in which activities such as conversations, walking, or eating take place after an individual is asleep.
Sleep-Eating
Other unusual behaviors include reports of individuals preparing and eating food after taking Ambien. Like sleepwalking, reports of any sleep-eating cases involve patients reporting that they were unaware at the time that they consumed any food. For example, a person who experiences sleep-eating due to Ambien use might find a half-eaten plate of food in the kitchen with no recollection of having prepared that food or eaten it. Sleep-eating can be harmful or detrimental to people who are trying to lose weight or have to stick to a particular diet for health purposes. For example, diabetic individuals need to regulate and keep tabs on the kind and amount of food they consume to ensure that their blood sugar levels remain stable. Another point of concern with sleep-eating is the risk of accidents when using appliances such as the stove or oven to prepare food. Individuals who are cooking in this sleep state where they may be less aware of their surroundings and circumstances could leave the oven or stove on, which could result in fires or other mishaps.
Sleep-Driving
Sleep-driving is probably one of the most notorious behaviors that can manifest as a side effect of Ambien. As previously mentioned, Ambien should not be mixed or combined with other drugs, especially central nervous system depressants. Besides amplifying the sedative effects in a person, the mixing of depressants with Ambien can also increase the chances of experiencing parasomnias, a word that describes the unusual experiences that occur when asleep such as sleep-eating or sleepwalking. Obviously, waking up behind the wheel unable to remember even getting into a car can be a very frightening experience. During these episodes, a person can leave their bed, enter their car, and simply start driving as they would normally. As previously mentioned, motor and cognitive impairment can last for up to several hours in the morning after taking a dose. Even if the user feels awake and alert, high doses of Ambien remain in the system for longer and can affect a user’s ability to properly operate a motor vehicle. Remaining mentally aware with functioning motor capabilities and normal reflex times are crucial to safe driving. The risk of an accident or getting pulled over for impaired driving can be higher when a user is attempting to drive with Ambien still in their system.
Engaging in Sexual Activity While Asleep
Individuals who have sex during a period of Ambien unawareness can be at a higher risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases and infections (STDs and STIs). Although it is usually a user’s partner that witnesses this kind of parasomnia, it is not impossible for a user to leave the house sleepwalking and initiate sexual activity with someone outside of the house. Northpoint Washington understands the seriousness of Ambien addiction and is here to help you. We have helped hundreds of people recover from addiction and go on to live healthier, happier lives. We’re here to help you with our integrated approach to addiction treatment. Start your Day One by calling 425.437.3298. 
Frequently Asked Questions:
Why is Ambien bad for you?
There are many negative consequences of taking Ambien recreationally. Although it is created to be used as a sleep aid, Ambien can induce feelings of euphoria upon taking it. These feelings will soon fade, only to be replaced with the typical drowsiness that Ambien is known for. Individuals who look towards Ambien misuse as a way to feel a rush of energy often take Ambien at very high doses. Frequent high doses of Ambien can result in severe side effects. Users can experience physical side effects such as headaches and lightheadedness. Cognitive side effects can also occur including amnesia, disorientation, and anxiety. Misusing Ambien also increases one’s chances of experiencing parasomnias, which are abnormal movements and actions undertaken when a person is sleeping. Parasomnias that can occur under the influence of Ambien can include sleepwalking, sleep-driving, sleep-eating, and engaging in sexual activity. Taking Ambien for a prolonged period at high doses can also increase a user’s chances of becoming addicted to the substance.
How long does Ambien make you sleep?
Although this might vary depending on the individual, general guidelines suggest that a person could sleep for about 7 to 8 hours with one dose. Of course, higher doses can increase that time. In addition, mixing Ambien with other central nervous system depressants such as alcohol or opioids can cause the sedative effects of Ambien to be magnified. Users should avoid mixing these substances to avoid possibilities of overdose and other adverse consequences.
How long does Ambien take to work on a full stomach?
Ambien can reach its peak effect anywhere from half an hour after initial ingestion to 1.5 hours later. Food can delay the absorption of the drug, so you may delay the medication for a bit after eating. However, if you are ready to go to bed and have just eaten, take the medication. Food only delays Ambien’s absorption a bit; it does not inhibit it completely.
What are the long-term effects of Ambien?
Individuals who misuse Ambien by taking it for a long period of time at high doses can experience side effects such as: hallucinations, dry mouth, continuous fatigue, anxiety, depression, persistent drowsiness, headaches, muscle pain, addiction, and withdrawal symptoms.
Is Ambien safe to take?
Ambien can have side effects—some severe—depending on the user’s behavior and circumstances. However, if a qualified doctor has determined that Ambien will work well for your situation, it should be safe to take according to the prescription instructions. Deviating from prescription instructions can lead to unwanted consequences and can be detrimental to the user’s health. To ensure the user’s health, follow the dosage instructions and listen to your doctor’s advice. Bring any concerns about the medication, including any strange side effects, to a medical professional.
What Did you Think About This Blog?
Give it a Rating!

